Today In History

Human history has been marked with events and activities that were too important to be forgotten or not written down. All of these were documented for future purposes, such as for your educational purpose. Irrespective of what kind of events they were; be they natural disasters, political actions, scientific inventions or anything at all, one thing that greatly differentiated us humans from animals is that ability to conceptualize our existence and pass that down to our offspring and future generations through documentations.
To ensure you learn a thing or two about previous event in our history, we’ve collated the largest collection of documented historical events all put in one place and accessible according to the day you are reading this content. For this reason, the large collection of daily historical events is known as Today In History. Alternatively, you could refer to it as ‘On This Day In History Funny Events’ if you are strictly looking for funny events that happened on this day in history.
The following Today In History Funny events are displayed according to whatever day you’re reading this content, it’ll only display events that happened on this specific day and month for several years behind.
On This Day In History
Events in history today, 26 of Feb
Valentinian I, sometimes known as Valentinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 364 to 375. He is the second-last emperor to govern the empire as a whole, albeit he only did so from February 26th to March 28th of 364, after which he appointed Valens to rule over the Eastern half the empire, while he remained in control of the West. During his reign, he fought successfully against the Alamanni, Quadi, and Sarmatians, strengthening the border fortifications and conducting campaigns across the Rhine and Danube. Also, his general Theodosius the Elder defeated a revolt in Africa and the Great Conspiracy. Valentinian founded the Valentinian dynasty, with his sons Gratian and Valentinian II succeeding him in the western half of the empire and his daughter Galla marrying emperor Theodosius I.
Valentinian I is proclaimed Roman emperor.
The Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty, also known as the Mongol–Jin War, was fought between the Mongol Empire and the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in Manchuria and North China. The war, which started in 1211, lasted over 23 years and ended with the complete conquest of the Jin dynasty by the Mongols in 1234.
Mongol-Jin War: The Mongols capture Kaifeng, the capital of the Jin dynasty, after besieging it for months.
The Battle of Benevento was a major medieval battle fought on 26 February 1266, near Benevento in present-day Southern Italy, between the forces of Charles I of Anjou and those of King Manfred of Sicily. Manfred's defeat and death resulted in Charles' conquest of the Kingdom of Sicily, effectively ending the rule of the Hohenstaufen dynasty in the Italian Peninsula and marking the rise of the royal Capetian House of Anjou. The engagement was part of the conflict which pitted Guelphs against Ghibellines.
Battle of Benevento: An army led by Charles, Count of Anjou, defeats a combined German and Sicilian force led by Manfred, King of Sicily. Manfred is killed in the battle and Pope Clement IV invests Charles as king of Sicily and Naples.
The Galileo affair was an early 17th century political, religious, and scientific controversy regarding the astronomer Galileo Galilei's defence of heliocentrism, the idea that the Earth revolves around the Sun. It pitted supporters and opponents of Galileo within both the Catholic Church and academia against each other through two phases: an interrogation and condemnation of Galileo's ideas by a panel of the Roman Inquisition in 1616, and a second trial in 1632 which led to Galileo's house arrest and a ban on his books.
Galileo Galilei is formally banned by the Roman Catholic Church from teaching or defending the view that the earth orbits the sun.
The first Christiansborg Palace in Copenhagen, Denmark, was built on Slotsholmen in 1745 as a new main residence for King Christian VI of Denmark-Norway. It was built on the same site as its predecessor, Copenhagen Castle, which had assumed a monstrous appearance and started to crumble under its own weight after several extensions.
The first Christiansborg Palace in Copenhagen burns down.
Napoleon Bonaparte, later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led a series of military campaigns across Europe during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars from 1796 to 1815. He led the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then ruled the French Empire as Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1814, and briefly again in 1815. He was King of Italy from 1805 to 1814, Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine from 1806 to 1813, and Mediator of the Swiss Confederation from 1803 to 1813.
Napoleon Bonaparte escapes from Elba.
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From August 1910 to September 1945, it included the Japanese archipelago, the Kurils, Karafuto, Korea, and Taiwan. The South Seas Mandate and concessions such as the Kwantung Leased Territory were de jure not internal parts of the empire but dependent territories. In the closing stages of World War II, with Japan defeated alongside the rest of the Axis powers, the formalized surrender was issued on September 2, 1945, in compliance with the Potsdam Declaration of the Allies, and the empire's territory subsequently shrunk to cover only the Japanese archipelago resembling modern Japan.
Japan and Korea sign a treaty granting Japanese citizens extraterritoriality rights, opening three ports to Japanese trade, and ending Korea's status as a tributary state of Qing dynasty China.
Kinemacolor was the first successful colour motion picture process. Used commercially from 1909 to 1915, it was invented by George Albert Smith in 1906. It was a two-colour additive colour process, photographing a black-and-white film behind alternating red/orange and blue/green filters and projecting them through red and green filters. It was demonstrated several times in 1908 and first shown to the public in 1909. From 1909 on, the process was known and trademarked as Kinemacolor and was marketed by Charles Urban's Natural Color Kinematograph Company, which sold Kinemacolor licences around the world.
Kinemacolor, the first successful color motion picture process, is first shown to the general public at the Palace Theatre in London.
HMHS Britannic was the third and final vessel of the White Star Line's Olympic class of ocean liners and the second White Star ship to bear the name Britannic. She was the younger sister of RMS Olympic and RMS Titanic and was intended to enter service as a transatlantic passenger liner. She operated as a hospital ship from 1915 until her sinking near the Greek island of Kea, in the Aegean Sea at position 37°42′05″N 24°17′02″E, in November 1916. At the time she was the largest hospital ship in the world, and the largest vessel built in Britain.
HMHS Britannic, sister to the RMS Titanic, is launched at Harland and Wolff shipyard in Belfast.
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only Democrat to serve as president during the Progressive Era, when Republicans dominated the presidency and legislative branches. As president, Wilson made significant economic reforms and led the United States through World War I. He was the leading architect of the League of Nations, and his stance on foreign policy came to be known as Wilsonianism.
President Woodrow Wilson signs an act of Congress establishing the Grand Canyon National Park.
Calvin Coolidge was the 30th president of the United States, serving from 1923 to 1929. A Republican lawyer from Massachusetts, he previously served as the 29th vice president from 1921 to 1923, under President Warren G. Harding, and as the 48th governor of Massachusetts from 1919 to 1921. Coolidge gained a reputation as a small-government conservative, with a taciturn personality and dry sense of humor that earned him the nickname "Silent Cal".
President Calvin Coolidge signs an executive order establishing the 96,000 acre Grand Teton National Park in Wyoming.
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Germany during the Nazi era, which lasted from 1933 until his suicide in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor of Germany in 1933 and then taking the title of Führer und Reichskanzler in 1934. Germany's invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 under his leadership marked the outbreak of the Second World War. Throughout the ensuing conflict, Hitler was closely involved in the direction of German military operations as well as the perpetration of the Holocaust, the genocide of about six million Jews and millions of other victims.
Adolf Hitler orders the Luftwaffe to be re-formed, violating the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles.
The February 26 incident , also known as the 2–26 incident, was an attempted coup d'état in the Empire of Japan on 26 February 1936. It was organized by a group of young Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) officers with the goal of purging the government and military leadership of their factional rivals and ideological opponents.
In the February 26 Incident, young Japanese military officers attempt to stage a coup against the government.
Alitalia - Società Aerea Italiana S.p.A., operating as Alitalia, was an Italian airline which was once the flag carrier and largest airline of Italy. The company had its head office in Fiumicino, in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital. The airline was owned by the Government of Italy as a nationalized business from its founding in 1946 until it was privatized in 2009. However, it struggled with profitability whilst operating as a private company, including failed negotiations to sell to other private parties. The airline entered extraordinary administration in 2017 following many years of financial losses. The Italian government eventually took back ownership of the airline in March 2020.
A New York-bound Alitalia airliner crashes into a cemetery in Shannon, Ireland, shortly after takeoff, killing 34 of the 52 persons on board.
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo was conceived during Project Mercury and executed after Project Gemini. It was conceived in 1960 as a three-person spacecraft during the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower. Apollo was later dedicated to President John F. Kennedy's national goal for the 1960s of "landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth" in an address to the U.S. Congress on May 25, 1961.
Apollo program: Launch of AS-201, the first flight of the Saturn IB rocket
The secretary-general of the United Nations is the Head of International Organization of the United Nations who Oversees the United Nations Secretariat, one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
U.N. Secretary-General U Thant signs United Nations proclamation of the vernal equinox as Earth Day.
The Superliner is a type of bilevel intercity railroad passenger car used by Amtrak, the national rail passenger carrier in the United States. Amtrak commissioned the cars to replace older single-level cars on its long-distance trains in the Western United States. The design was based on the Budd Hi-Level cars used by the Santa Fe Railway on its El Capitan trains. Pullman-Standard built 284 cars, known as Superliner I, from 1975 to 1981; Bombardier Transportation built 195, known as Superliner II, from 1991 to 1996. The Superliner I cars were the last passenger cars built by Pullman.
The Superliner railcar enters revenue service with Amtrak.
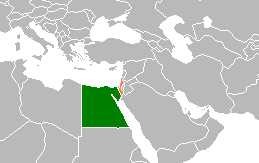
Foreign relations between Egypt and Israel, which dated back to the 1948 Arab–Israeli War culminated in the Yom Kippur War in 1973, and was followed by the 1979 Egypt–Israel peace treaty a year after the Camp David Accords, mediated by U.S. president Jimmy Carter. Full diplomatic relations were established on January 26, 1980, and the formal exchange of ambassadors took place one month later, on February 26, 1980, with Eliyahu Ben-Elissar serving as the first Israeli Ambassador to Egypt, and Saad Mortada as the first Egyptian Ambassador to Israel. Egypt has an embassy in Tel Aviv and a consulate in Eilat. Israel has an embassy in Cairo and a consulate in Alexandria. Their shared border has two official crossings, one at Taba and one at Nitzana. The crossing at Nitzana is for commercial and tourist traffic only. The two countries' borders also meet at the shoreline of the Gulf of Aqaba in the Red Sea.
Egypt and Israel establish full diplomatic relations.
The Iran–Contra affair, also referred to as the Iran–Contra scandal, the Contragate, Iran Initiative, or simply Iran–Contra, was a political scandal in the United States that centered on arms trafficking to Iran between 1981 and 1986, facilitated by senior officials of the Reagan administration. The administration hoped to use the proceeds of the arms sale to fund the Contras, an anti-Sandinista rebel group in Nicaragua. Under the Boland Amendments, a series of laws passed by Congress and signed by Ronald Reagan, further funding of the Contras by legislative appropriations was prohibited by Congress, but the Reagan administration continued funding them secretly using non-appropriated funds.
Iran-Contra affair: The Tower Commission rebukes President Ronald Reagan for not controlling his national security staff.
On February 26, 1993, Ramzi Yousef and associates carried out a van bomb terrorist attack below the North Tower of the World Trade Center in New York City. The 1,336-pound (606 kg) urea nitrate–hydrogen gas enhanced device was intended to make the North Tower collapse onto the South Tower, taking down both skyscrapers and killing tens of thousands of people. While it failed to do so, it was successful in killing six people, and caused over a thousand injuries. About 50,000 people were evacuated from the buildings that day.
World Trade Center bombing: In New York City, a truck bomb parked below the North Tower of the World Trade Center explodes, killing six and injuring over a thousand.
Barings Bank was a British merchant bank based in London. It was one of England's oldest merchant banks after Berenberg Bank, Barings' close collaborator and German representative. It was founded in 1762 by Francis Baring, a British-born member of the German–British Baring family of merchants and bankers.
The UK's oldest investment banking institute, Barings Bank, collapses after a rogue securities broker Nick Leeson loses $1.4 billion by speculating on the Singapore International Monetary Exchange using futures contracts.
Keddies was a small chain of department stores in Essex, England, with its flagship store in a prime location in Southend High Street. The business had a national reputation, being recognised in The Fashion Handbook, appearing on the side of a Matchbox model 17C bus and being one of the retailers that fought to remove Retail Price Maintenance. The business grew in the 1970s opening further branches across Essex, before closing them during the 1980s. Keddies closed for business on 26 February 1996 after going into administration.
Keddies, the Southend-on-Sea department store closes it doors after 104 years of trading.
The New York Philharmonic is an American symphony orchestra based in New York City. Known officially as the Philharmonic-Symphony Society of New York, Inc., and globally known as the New York Philharmonic Orchestra (NYPO) or the New York Philharmonic-Symphony Orchestra, it is one of the leading American orchestras popularly called the "Big Five". The Philharmonic's home is David Geffen Hall, at New York's Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts.
The New York Philharmonic performs in Pyongyang, North Korea; this is the first event of its kind to take place in North Korea.
The Burlington VIA train derailment was a derailment that occurred on February 26, 2012, in the Aldershot neighbourhood of Burlington, Ontario, Canada, resulting in deaths of the 3 engineers in the locomotive and 46 injuries. There were 75 passengers and four crew members on board at the time of the accident. The derailment occurred in an industrial area east of Aldershot GO Station. The official report into the accident was released on June 10, 2013, by the Transportation Safety Board of Canada (TSB) indicating that the crew misinterpreted the signal causing them to believe that they were authorized to proceed at track speed, when in fact they were authorized only for slow speed—a maximum of 15 mph (24 km/h)—in order to switch tracks.
A train derails in Burlington, Ontario, Canada killing at least three people and injuring 45.
A hot air balloon is a lighter-than-air aircraft consisting of a bag, called an envelope, which contains heated air. Suspended beneath is a gondola or wicker basket, which carries passengers and a source of heat, in most cases an open flame caused by burning liquid propane. The heated air inside the envelope makes it buoyant, since it has a lower density than the colder air outside the envelope. As with all aircraft, hot air balloons cannot fly beyond the atmosphere. The envelope does not have to be sealed at the bottom, since the air inside the envelope is at about the same pressure as the surrounding air. In modern sport balloons the envelope is generally made from nylon fabric, and the inlet of the balloon is made from a fire-resistant material such as Nomex. Modern balloons have been made in many shapes, such as rocket ships and the shapes of various commercial products, though the traditional shape is used for most non-commercial and many commercial applications.
A hot air balloon crashes near Luxor, Egypt, killing 19 people.
Don’t Forget to share these On This Day In History event and facts with your family and friends who love to learn from historical events.